Parallel computing : use of multiple processors or computers working together on a common task.
Today, commercial applications provide an equal or greater driving force in the development of faster computers. These applications require the processing of large amounts of data in sophisticated ways. For example:
a. Parallelism Concept
When performing task, some subtasks depend on one another, while others do not.
Example: Preparing dinner
b. Distributed Processing
GPU (Graphical Processing Unit) processor initially is a special function for rendering the graphics card alone, but along with the increasing need for rendering, particularly for approaching realtime processing time, it also increases the ability of the graphics processor. GPU acceleration technology improvement is much faster than the increase in the actual processor technology (CPU), and eventually became the General Purpose GPU, which means it is no longer just for rendering only but can be used for general computing process.
The use of Multi GPU can accelerate the processing time for executing programs natively parallel architecture. In addition to the improvements in performance that occurs not only by the speed of the GPU hardware, but the more important factor is how to create code that can be truly effective running on Multi GPU.
CUDA is a new technology from Nvidia graphics card manufacturers, and may not have been widely used by people in general. The graphics card is more widely used for applications running game, but with this CUDA graphics card can be used more optimally when running a software application. Nvidia graphics card functions are used to help Processor (CPU) to perform calculations on the data process.
CUDA stands for Compute Unified Device Architecture from, is defined as a parallel computer architecture, developed by Nvidia. This technology can be used to perform image processing, video, 3D rendering, and so forth. VGA - VGA Nvidia are already using CUDA technology, among others: Nvidia GeForce GTX 280, GTX 260.9800 GX2, 9800 GTX +, 9800 GTX, 9800 GT, 9600 GSO, 9600 GT, 9500 GT, 9400 GT, 9400 mGPU, 9300 mGPU , 8800 Ultra, 8800 GTX, 8800 GTS, 8800 GT, 8800 GS, 8600 GTS, 8600 GT, 8500 GT, 8400 GS, 8300 mGPU, 8200 mGPU, 8100 mGPU, and a similar series for the mobile class (notebook VGA).
In short, CUDA can provide the process with the approach of the C language, so the programmer or software developer can more quickly complete complex calculations. Not only technological applications such specific knowledge. CUDA can now be used for multimedia applications. For example, to edit the film and perform image filters. For example, with multimedia applications, are already using CUDA technology. TMPGEnc 4.0 software makes editing applications eg by taking some proces of GPU and CPU. VGA can take advantage of CUDA only 8000 or higher version.
reference:
- reference 1
- reference 2
- reference 3
- reference 4
- reference 5
[ Read More ]
- Each processor works on its section of the problem
- Processors can exchange information
Today, commercial applications provide an equal or greater driving force in the development of faster computers. These applications require the processing of large amounts of data in sophisticated ways. For example:
- Databases, data mining
- Oil exploration
- Web search engines, web based business services
- Medical imaging and diagnosis
- Management of national and multi-national corporations
- Financial and economic modeling
a. Parallelism Concept
When performing task, some subtasks depend on one another, while others do not.
Example: Preparing dinner
- Salad prep independent of lasagna baking
- Lasagna must be assembled before baking
b. Distributed Processing
Distributed computing studies separate processors connected by communication links. Whereas
parallel processing models often (but not always) assume shared memory,
distributed systems rely fundamentally on message passing. Distributed
systems are inherently concurrent. Like concurrency, distribution is
often part of the goal, not solely part of the solution: if resources
are in geographically distinct locations, the system is inherently
distributed. Systems in which partial failures (of processor nodes or of
communication links) are possible fall under this domain.
Shared and distributed memory
c. Architectural Parallel Computer
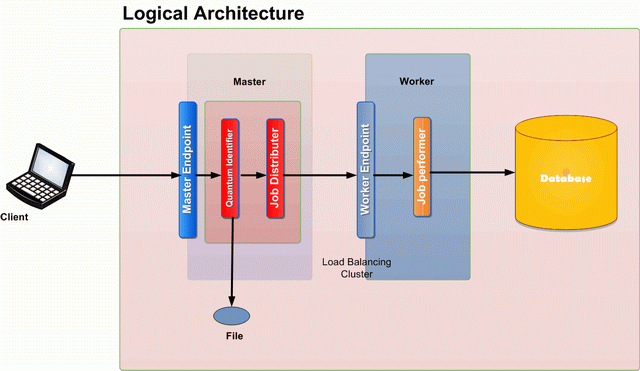
A client machine initiates a request to process a file. The mechanism about how the client comes to know that a file is available for processing is immaterial. The WCF service must have access rights to the requested file.
The application has two WCF services, the master and the worker. The job of the master is to expose an end point using which requests are initiated.
The Master WCF service has a Quantum Identifier component; this is responsible for identifying independent quantum of task. In our application, this will be the module which will read the file line by line and send each line for processing.
The Job distributor is responsible for sending the task to a worker in an async manner. The Job distributor may or may not expect a result from the worker which leads to a decision of async or OneWay method.
The worker has a WCF endpoint which is used by the Master for requesting a quantum task for processing. The Job Performer is used for the component which executes the tasks.
In an ideal scenario, many identical workers are deployed behind a load balancing cluster.
The application has two WCF services, the master and the worker. The job of the master is to expose an end point using which requests are initiated.
The Master WCF service has a Quantum Identifier component; this is responsible for identifying independent quantum of task. In our application, this will be the module which will read the file line by line and send each line for processing.
The Job distributor is responsible for sending the task to a worker in an async manner. The Job distributor may or may not expect a result from the worker which leads to a decision of async or OneWay method.
The worker has a WCF endpoint which is used by the Master for requesting a quantum task for processing. The Job Performer is used for the component which executes the tasks.
In an ideal scenario, many identical workers are deployed behind a load balancing cluster.
d. Introduction Thread Programming
Threading / Thread is a control flow of a process. 2 The concept of threading is a running process (a process similar or different processes) at one time. For example, a web browser that has a thread for displaying images or text while another thread serves as the receiving data from the network. Threading is divided into two:
Static Threading
This technique is commonly used for chip multiprocessors and computer with a shared-memory computer types other. This technique allows a thread to share the available memory, using a program counter and executing the program independently. The operating system puts a thread on the processor and replace it with other threads that want to use the processor.
This technique is commonly used for chip multiprocessors and computer with a shared-memory computer types other. This technique allows a thread to share the available memory, using a program counter and executing the program independently. The operating system puts a thread on the processor and replace it with other threads that want to use the processor.
Dynamic Multithreading
This technique is an extension of previous techniques that aim to ease with her because the programmer does not have to bother with communication protocols, load balancing, and other complexity that exist in static threading. Concurrency this platform provides a scheduler that performs automatic load balacing. Although the platform is still in development but generally supports two features: nested parallelism and parallel loops
This technique is an extension of previous techniques that aim to ease with her because the programmer does not have to bother with communication protocols, load balancing, and other complexity that exist in static threading. Concurrency this platform provides a scheduler that performs automatic load balacing. Although the platform is still in development but generally supports two features: nested parallelism and parallel loops
e. CUDA GPU Programming
GPU (Graphical Processing Unit) processor initially is a special function for rendering the graphics card alone, but along with the increasing need for rendering, particularly for approaching realtime processing time, it also increases the ability of the graphics processor. GPU acceleration technology improvement is much faster than the increase in the actual processor technology (CPU), and eventually became the General Purpose GPU, which means it is no longer just for rendering only but can be used for general computing process.
The use of Multi GPU can accelerate the processing time for executing programs natively parallel architecture. In addition to the improvements in performance that occurs not only by the speed of the GPU hardware, but the more important factor is how to create code that can be truly effective running on Multi GPU.
CUDA is a new technology from Nvidia graphics card manufacturers, and may not have been widely used by people in general. The graphics card is more widely used for applications running game, but with this CUDA graphics card can be used more optimally when running a software application. Nvidia graphics card functions are used to help Processor (CPU) to perform calculations on the data process.
CUDA stands for Compute Unified Device Architecture from, is defined as a parallel computer architecture, developed by Nvidia. This technology can be used to perform image processing, video, 3D rendering, and so forth. VGA - VGA Nvidia are already using CUDA technology, among others: Nvidia GeForce GTX 280, GTX 260.9800 GX2, 9800 GTX +, 9800 GTX, 9800 GT, 9600 GSO, 9600 GT, 9500 GT, 9400 GT, 9400 mGPU, 9300 mGPU , 8800 Ultra, 8800 GTX, 8800 GTS, 8800 GT, 8800 GS, 8600 GTS, 8600 GT, 8500 GT, 8400 GS, 8300 mGPU, 8200 mGPU, 8100 mGPU, and a similar series for the mobile class (notebook VGA).
In short, CUDA can provide the process with the approach of the C language, so the programmer or software developer can more quickly complete complex calculations. Not only technological applications such specific knowledge. CUDA can now be used for multimedia applications. For example, to edit the film and perform image filters. For example, with multimedia applications, are already using CUDA technology. TMPGEnc 4.0 software makes editing applications eg by taking some proces of GPU and CPU. VGA can take advantage of CUDA only 8000 or higher version.
reference:
- reference 1
- reference 2
- reference 3
- reference 4
- reference 5